문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/10026

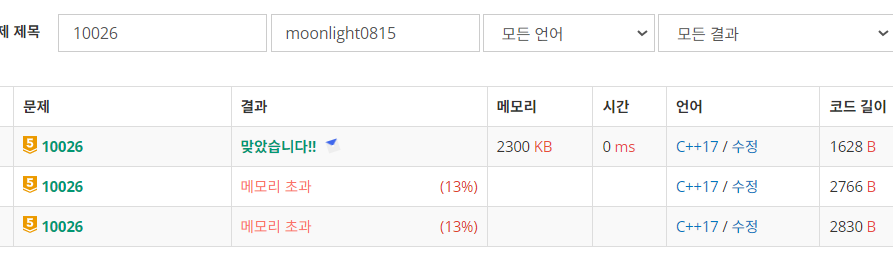
구상
기본적 flood fill문제였다. 몇개의 섬이 있는지 판단하면 되는, 정말 간단한 문제였다. 그냥 문제 읽자마자 flood fill이라는 걸 알 수 있었다. 그리고, 아래를 보면 알 수 있다 싶이 bfs로 풀게 되면 메모리 초과가 났다. dfs로 풀어야 한정된 메모리 안에서 풀렸다.
코드 + 풀이
1) 메모리초과 난 BFS 풀이
BFS가 너비 우선 탐색으로 인해 많은 노드를 메모리(큐)에 저장해야 해서 노드의 연결이 많을 경우, 저장되는 노드 수가 많아져, 메모리 초과의 가능성이 있다.
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#define MAX 101
#define endl "\n"
using namespace std;
/*
10026 적록색약
그림이 입력으로 주어졌을 때, 적록 색약인 사람이 봤을 때와 아닌 사람이 봤을 때 구역의 수를 구하자 -> flood fill
시간초과 나는 bfs 풀이
*/
int N; // 1~100
vector<vector<char>> map_n;
vector<vector<char>> map_y;
vector<pair<int, int>> dxy = { {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1} };
void numberingLand(int y, int x, int count, char c, vector<vector<char>>& map) { // bfs로 인접한 같은 땅에 같은 번호 부여하기
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({ x, y });
map[y][x] = count; // 방문 표시
while (!q.empty()) {
int xx = q.front().first;
int yy = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = xx + dxy[i].first;
int ny = yy + dxy[i].second;
// 경계값 확인
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < N && ny < N) {
// 같은 영역이고 방문하지 않았을 때
if (map[ny][nx] == c) {
map[ny][nx] = count; // 방문 표시
q.push({ nx, ny });
}
}
}
}
}
void solution() {
// 적록색약이 아닌 사람
int count_n = 1; // 1부터 시작 (방문 표시용 숫자)
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (map_n[i][j] == 'R' || map_n[i][j] == 'G' || map_n[i][j] == 'B') {
numberingLand(i, j, count_n, map_n[i][j], map_n);
count_n++;
}
}
}
cout << count_n - 1 << " "; // 시작이 1이었으므로, 결과에서 1을 뺀다
// 적록색약인 사람 -> R, G를 같은 것으로 봄
int count_y = 1; // 1부터 시작 (방문 표시용 숫자)
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (map_y[i][j] == 'R' || map_y[i][j] == 'B') {
numberingLand(i, j, count_y, map_y[i][j], map_y);
count_y++;
}
}
}
cout << count_y - 1 << endl; // 시작이 1이었으므로, 결과에서 1을 뺀다
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
// 입력
cin >> N;
map_n.resize(N, vector<char>(N));
map_y.resize(N, vector<char>(N));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map_n[i][j] = str[j];
if (str[j] == 'R' || str[j] == 'G')
map_y[i][j] = 'R'; // 적록색약인 사람은 R과 G를 동일하게 봄
else
map_y[i][j] = str[j];
}
}
// 로직
solution();
return 0;
}
2) 메모리 줄인 DFS 풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define MAX 100
using namespace std;
int N;
vector<vector<char>> map_n;
vector<vector<char>> map_y;
vector<pair<int, int>> dxy = { {1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1} };
void dfs(int x, int y, char color, vector<vector<char>>& map) {
map[x][y] = '0'; // 방문 표시
for (auto dir : dxy) {
int nx = x + dir.first;
int ny = y + dir.second;
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < N && ny < N && map[nx][ny] == color) {
dfs(nx, ny, color, map);
}
}
}
void solution() {
int count_n = 0;
int count_y = 0;
// 적록색약이 아닌 사람
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (map_n[i][j] != '0') {
dfs(i, j, map_n[i][j], map_n);
count_n++;
}
}
}
// 적록색약인 사람
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (map_y[i][j] != '0') {
dfs(i, j, map_y[i][j], map_y);
count_y++;
}
}
}
cout << count_n << " " << count_y << endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> N;
map_n.resize(N, vector<char>(N));
map_y.resize(N, vector<char>(N));
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
string str;
cin >> str;
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
map_n[i][j] = str[j];
map_y[i][j] = (str[j] == 'G') ? 'R' : str[j]; // 적록색약인 사람은 'R'과 'G'를 동일하게 봄
}
}
solution();
return 0;
}
메모리 사용 차이
BFS
- BFS는 너비 우선 탐색이기 때문에 각 레벨의 모든 노드를 메모리에 저장해야 한다.
- 예를 들어, 최악의 경우 트리의 마지막 레벨에 있는 모든 노드를 저장해야 할 수도 있다. 이 경우 메모리 사용량이 급격히 증가한다.
- 특히 N이 크고 노드의 연결이 많은 경우, 큐에 저장되는 노드 수가 많아져 메모리 초과가 발생할 수 있다.
DFS
- DFS는 깊이 우선 탐색이기 때문에, 한 경로를 끝까지 탐색한 후 다른 경로를 탐색한다.
- 재귀 호출을 사용하여 스택을 관리하면, 시스템 스택을 사용하게 되므로 메모리 사용량이 상대적으로 적다.
- 일반적으로 한 경로의 깊이만큼만 메모리를 사용하므로, BFS보다 메모리 사용량이 적게 된다.
'알고리즘 > 문제풀이' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준/C++] #1913 달팽이 (Simulation) (0) | 2024.08.05 |
|---|---|
| [코드트리/C++] 배열 회전 (Simulation) (0) | 2024.08.05 |
| [백준/C++] #16933 벽 부수고 이동하기 2, 3 (BFS) (0) | 2024.07.31 |
| [백준/C++] #1509 팰린드롬 분할 (DP) (9) | 2024.07.24 |
| [백준/C++] #11049 행렬 곱셈 순서 (DP) (0) | 2024.07.23 |



